Hearing Aids 101
3 min read
Hearing aids have undergone numerous advancements over the years. From bulky devices of the past to today’s sleek digital hearing aids, the journey to better hearing is smoother than ever. If you’re struggling with hearing loss, learn more about hearing aids and understand your options to help you make the best choice for your auditory needs.
In comparison, OTC hearing aids are available to anyone 18 years and over with mild to moderate hearing loss. These are designed for general use rather than being tailored to your individual needs. Since they can be purchased without a prescription, they often come with a lower upfront cost. But because they aren’t custom, you won’t enjoy the same auditory clarity as a prescription device.
Hearing Aid Basics
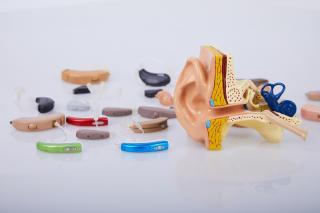
A hearing aid is an electronic device that amplifies sound, helping people with hearing loss perceive sound and understand speech more clearly. The main components of any hearing aid include a microphone, amplifier, speaker, battery, and computer processor.Types of Hearing Aids
Today’s hearing aids come in wide-ranging styles and sizes. Here are some examples:- Behind-the-ear (BTE) devices are the most common hearing aids, suitable for people of all ages with different types of hearing loss. The main component rests behind the ear, with a clear tube directing sound into the canal.
- In-the-canal (ITC) and completely-in-the-canal (CIC) devices are molded to fit deep inside your ear and are virtually invisible to onlookers.
- In-the-ear (ITE) devices are customized to fit within the outer ear. These hearing aids are easier to handle and have a longer battery life than their ITC and CIC counterparts.
- Nano hearing aids are a relatively new addition. These tiny, discreet hearing aids offer state-of-the-art technology for optimal sound clarity.
Key Hearing Aid Features to Look For
Modern hearing aids come with a suite of advanced features. Some of the most in-demand options include:- Rechargeable batteries: Say goodbye to constantly changing hearing aid batteries. When you can recharge your hearing aid, you reduce waste and save money on replacement batteries.
- Bluetooth hearing aid: Seamlessly connect your hearing aids to Bluetooth-enabled devices like phones, TVs, and music players for an enhanced auditory experience.
- Adjustability: Hearing aids with multiple listening programs are adjustable based on your environment. Some devices auto-switch according to ambient conditions, while others have remote controls for manual adjustments.
Prescription vs. OTC Hearing Aids
Many people are surprised to learn that hearing aids come in prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) versions. Prescription hearing aids are purchased through an audiologist after undergoing a thorough hearing evaluation. These are customized solutions tailored to your specific hearing loss and ear anatomy.In comparison, OTC hearing aids are available to anyone 18 years and over with mild to moderate hearing loss. These are designed for general use rather than being tailored to your individual needs. Since they can be purchased without a prescription, they often come with a lower upfront cost. But because they aren’t custom, you won’t enjoy the same auditory clarity as a prescription device.
